| Home |
| Apple |
5. Stem Borer |
6. Fruitfly |
9. Leaf Miner |
10. Psyllid |
| Questions |
| Download Notes |
Pests of Apple :: Major Pest :: Apple Codling Moth
4. Apple Codling Moth: Cydia pomonella (Tortricidae: Lepidoptera) Distribution and status: Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Tamil Nadu Damage symptoms |
 |
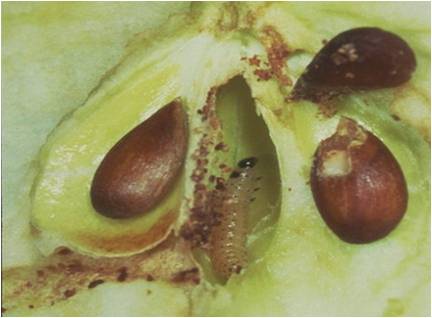
It causes two types of fruit damage: stings and deep entries. Stings are entries where larvae bore into the flesh a short distance before dying. Deep entries occur when larvae penetrate the fruit skin, bore to the core, and feed in the seed cavity. Young larvae enters the fruit thorugh calyx penetrates and attacks the core and flesh. Larvae may enter through the sides, stem end, or calyx end of the fruit. One or more holes plugged with frass on the fruit's surface are a characteristic sign of codling moth infestation. Calyx entries are difficult to detect without cutting the fruit. |
Bionomics |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Female lays 100 white coloured, oval, flat eggs, singly on developing fruits, leaves and twigs. Egg period 4-12 days, larval period 21-30 days and pupal period 8-14 days. Grown up larvae comes out of the fruit and falls on ground and reach the bark of the tree for shelter in cracks and crevices to construct a silken cocoon and transforms to a yellowish brown pupa.
Management Kill larvae by mopping up with a pole and some rags dipped in kerosene tied on its end.
|
|