| Home |
| Apple |
5. Stem Borer |
6. Fruitfly |
9. Leaf Miner |
10. Psyllid |
| Questions |
| Download Notes |
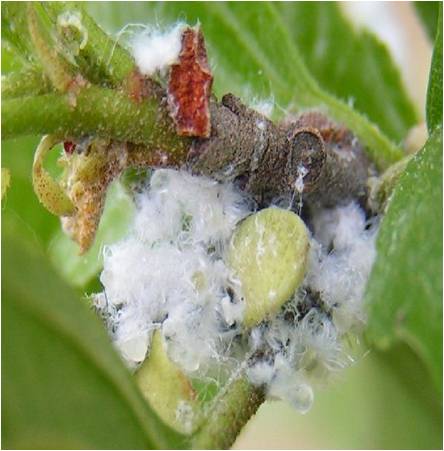
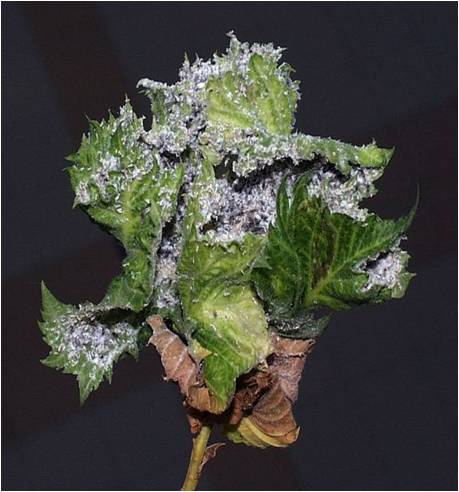
Pests of Apple :: Major Pest :: Apple Woolly Aphid
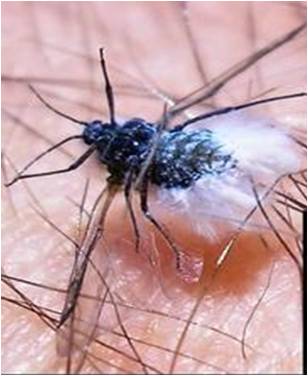
1. Apple woolly aphid: Eriosoma lanigerum (Pemphigidae: Hemiptera) Distribution and status: Hilly tracts in India and world
Damage symptoms |
||
 |
 |
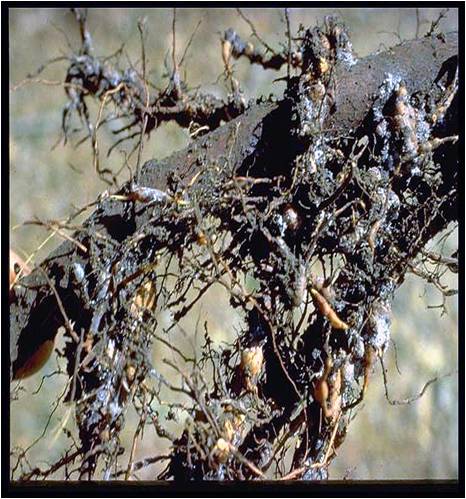 |
Sap sucking by nymphs and adults results in weakening and death of the smaller plants; galls on the roots and white woolly patches on the trunk. Aphids suck cell sap from the bark of the twigs and from the roots underground. Swelling or knots appear on the roots which hinder the normal plant functions. Aphids crowd together covered with wooly white patches on the trunk.
Bionomics
|
||
 |
 |
 |
Reproduction is both sexual and asexual but mostly by parthenogenesis. Aphid is active throughout the year except in cold months of December and January. Wingless forms are present throughout the year whereas winged forms are seen from July to October. Alate form disperses by flight and gives rise to apterous forms by sexual reproduction. In winter, colonies on the tree trunks move to the base of the trunk just below the soil. Female produces 116 young ones, nymphal period 35-42 days with four instars.
Management
|
||